Basic to Intermediate Level
Attendees knowledge of this course steps forward from Beginners level to Intermediate level user of Microsoft Excel.
WHO SHOULD ATTEND
This course is important for those who are using Excel as their basic working tool and want to step ahead by learning smart ways. After learning skills in this course and by efficiently use them can save at-least 4 to 5 hours weekly.
Beginner users who have basic knowledge of Excel and can make basic calculations.
WHAT YOU WILL BE ABLE TO DO
Environment:
- Better understanding of Excel 2016 interface
- Easily working around with Excel environment (e.g. rows/columns/etc, selections)
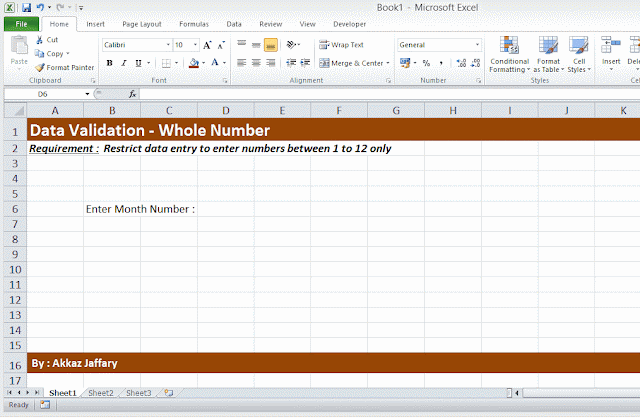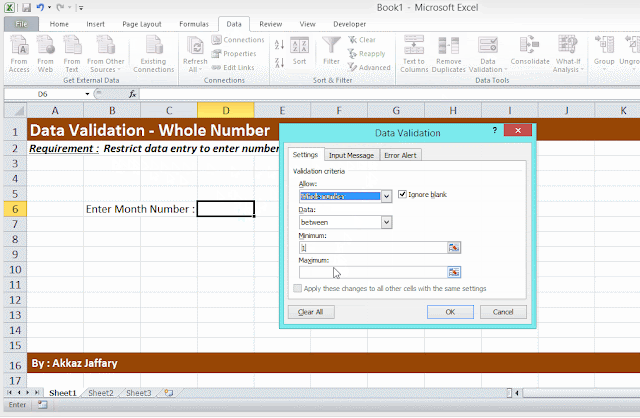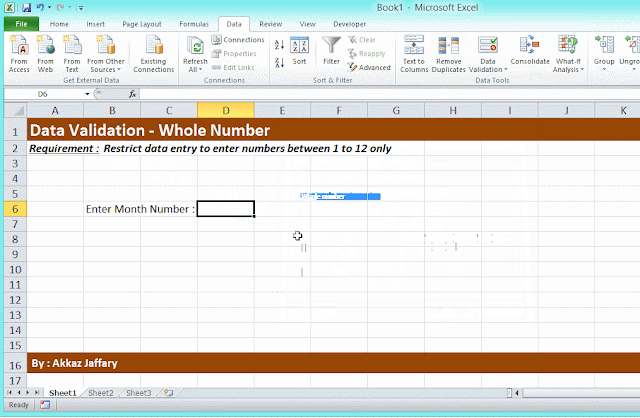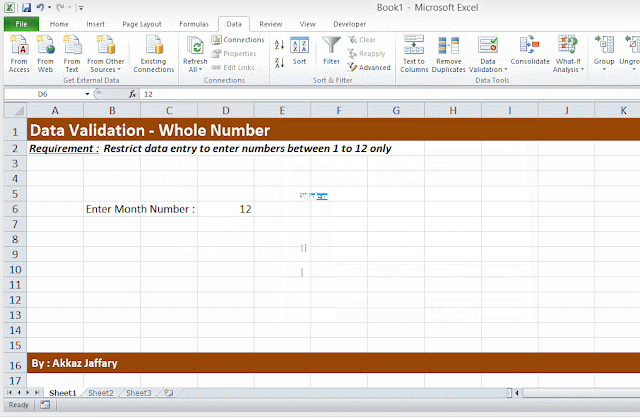
- Secure data and/or restrict your users to post data within required cells only.
Data & File Handling:
- Change the order of data
- View part of data based on criterias
- Reports Preparations (Data and Cell Formatting),
- Page Setup, File handling and Printing.
Formulas:
Formulas make Excel a smart spreadsheet program. In this course you will learn ...
Formulas make Excel a smart spreadsheet program. In this course you will learn ...
- Fundamentals of formulas and functions.
- Simple and complex formulas introduction
- Cell Referencing, its types and their usages.
- Auto & quick SUMs, other basic functions.
Charts:
- Introduction to data visualization with Charts
- Ability of select appropriate chart, which is suitable for which data
- Create Column, Bar, Line and Pie graphs.
- Customization
To register yourself in upcomming sessions fill the below form for registration...
<...>
*int_v2*